Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
What is Problem-Based Learning (PBL)? PBL is a student-centered approach to learning that involves groups of students working to solve a real-world problem, quite different from the direct teaching method of a teacher presenting facts and concepts about a specific subject to a classroom of students. Through PBL, students not only strengthen their teamwork, communication, and research skills, but they also sharpen their critical thinking and problem-solving abilities essential for life-long learning. See also: Just-in-Time Teaching 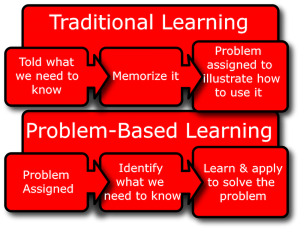 In implementing PBL, the teaching role shifts from that of the more traditional model that follows a linear, sequential pattern where the teacher presents relevant material, informs the class what needs to be done, and provides details and information for students to apply their knowledge to a given problem. With PBL, the teacher acts as a facilitator; the learning is student-driven with the aim of solving the given problem (note: the problem is established at the onset of learning opposed to being presented last in the traditional model). Also, the assignments vary in length from relatively short to an entire semester with daily instructional time structured for group work.
In implementing PBL, the teaching role shifts from that of the more traditional model that follows a linear, sequential pattern where the teacher presents relevant material, informs the class what needs to be done, and provides details and information for students to apply their knowledge to a given problem. With PBL, the teacher acts as a facilitator; the learning is student-driven with the aim of solving the given problem (note: the problem is established at the onset of learning opposed to being presented last in the traditional model). Also, the assignments vary in length from relatively short to an entire semester with daily instructional time structured for group work. 
By working with PBL, students will:
- Become engaged with open-ended situations that assimilate the world of work
- Participate in groups to pinpoint what is known/ not known and the methods of finding information to help solve the given problem.
- Investigate a problem; through critical thinking and problem solving, brainstorm a list of unique solutions.
- Analyze the situation to see if the real problem is framed or if there are other problems that need to be solved.
How to Begin PBL
- Establish the learning outcomes (i.e., what is it that you want your students to really learn and to be able to do after completing the learning project).
- Find a real-world problem that is relevant to the students; often the problems are ones that students may encounter in their own life or future career.
- Discuss pertinent rules for working in groups to maximize learning success.
- Practice group processes: listening, involving others, assessing their work/peers.
- Explore different roles for students to accomplish the work that needs to be done and/or to see the problem from various perspectives depending on the problem (e.g., for a problem about pollution, different roles may be a mayor, business owner, parent, child, neighboring city government officials, etc.).
- Determine how the project will be evaluated and assessed. Most likely, both self-assessment and peer-assessment will factor into the assignment grade.
Designing Classroom Instruction
- Take the curriculum and divide it into various units. Decide on the types of problems that your
students will solve. These will be your objectives.
- Determine the specific problems that most likely have several answers; consider student interest.
- Arrange appropriate resources available to students; utilize other teaching personnel to support students where needed (e.g., media specialists to orientate students to electronic references).
- Decide on presentation formats to communicate learning (e.g., individual paper, group PowerPoint, an online blog, etc.) and appropriate grading mechanisms (e.g., rubric).
- Decide how to incorporate group participation (e.g., what percent, possible peer evaluation, etc.).
How to Orchestrate a PBL Activity
- Explain Problem-Based Learning to students: its rationale, daily instruction, class expectations, grading.
- Serve as a model and resource to the PBL process; work in-tandem through the first problem
- Help students secure various resources when needed.
- Supply ample class time for collaborative group work.
- Give feedback to each group after they share via the established format; critique the solution in quality and thoroughness. Reinforce to the students that the prior thinking and reasoning process in addition to the solution are important as well.
Teacher’s Role in PBL
As previously mentioned, the teacher determines a problem that is interesting, relevant, and novel for the students. It also must be multi-faceted enough to engage students in doing research and finding several solutions. The problems stem from the unit curriculum and reflect possible use in future work situations.
- Determine a problem aligned with the course and your students. The problem needs to be demanding enough that the students most likely cannot solve it on their own. It also needs to teach them new skills. When sharing the problem with students, state it in a narrative complete with pertinent background information without excessive information. Allow the students to find out more details as they work on the problem.
- Place students in groups, well-mixed in diversity and skill levels, to strengthen the groups. Help students work successfully. One way is to have the students take on various roles in the group process after they self-assess their strengths and weaknesses.
- Support the students with understanding the content on a deeper level and in ways to best orchestrate the various stages of the problem-solving process.
The Role of the Students
The students work collaboratively on all facets of the problem to determine the best possible solution.
 In implementing PBL, the teaching role shifts from that of the more traditional model that follows a linear, sequential pattern where the teacher presents relevant material, informs the class what needs to be done, and provides details and information for students to apply their knowledge to a given problem. With PBL, the teacher acts as a facilitator; the learning is student-driven with the aim of solving the given problem (note: the problem is established at the onset of learning opposed to being presented last in the traditional model). Also, the assignments vary in length from relatively short to an entire semester with daily instructional time structured for group work.
In implementing PBL, the teaching role shifts from that of the more traditional model that follows a linear, sequential pattern where the teacher presents relevant material, informs the class what needs to be done, and provides details and information for students to apply their knowledge to a given problem. With PBL, the teacher acts as a facilitator; the learning is student-driven with the aim of solving the given problem (note: the problem is established at the onset of learning opposed to being presented last in the traditional model). Also, the assignments vary in length from relatively short to an entire semester with daily instructional time structured for group work. 